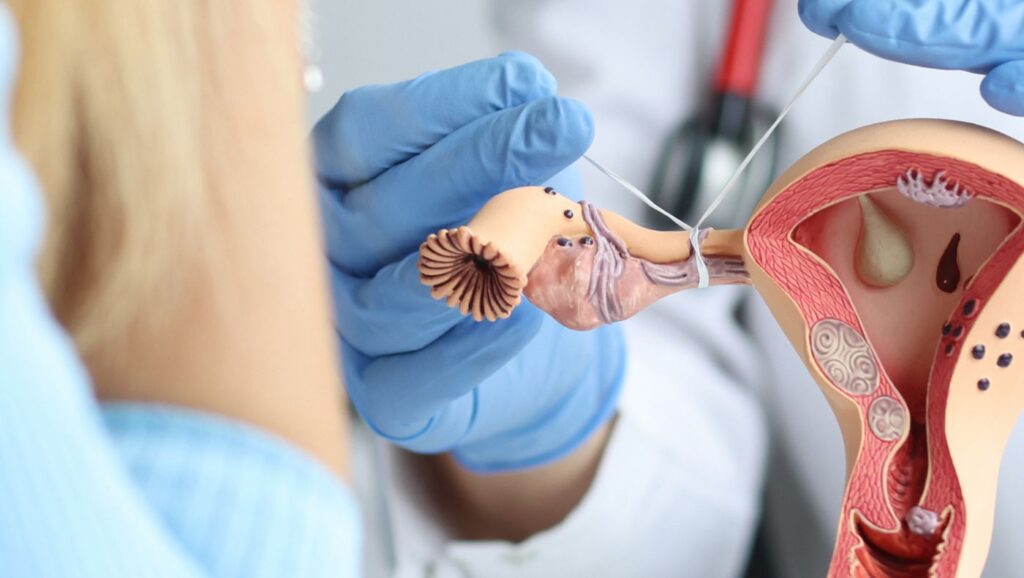
Introduction: Cornual Block in Fallopian Tube: Impact on Fertility
The cornual block in the fallopian tube is a condition that can significantly impact a woman’s fertility and reproductive health. Located at the junction where the fallopian tubes connect to the uterus, the cornua of the fallopian tubes play a crucial role in the process of conception, facilitating the passage of sperm toward the egg and the transport of the fertilized egg to the uterus. A cornual block can occur unilaterally or bilaterally, leading to potential complications such as ectopic pregnancies or infertility due to the obstruction of the egg’s journey. Understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatment options for cornual block is essential for those seeking to overcome fertility challenges and achieve pregnancy. In this exploration, we will delve into the nature of cornual block, its effects on reproductive health, and the available avenues for treatment to restore fertility.
What is a Cornual Block?
A cornual block refers to an obstruction that occurs at the cornua of the fallopian tubes. The cornua are the areas where the fallopian tubes connect to the uterus. When a block occurs here, it can hinder the passage of eggs from the ovaries into the uterus, potentially leading to fertility issues. This condition can be caused by various factors, including infections, scarring from previous surgeries, endometriosis, or congenital abnormalities. Diagnosing a cornual block typically involves imaging techniques such as hysterosalpingography (HSG) or laparoscopy.
The Role of the Cornua in Fallopian Tubes
The cornua play a crucial role in reproductive health. As the entry point for the fallopian tubes into the uterus, they facilitate the transport of the egg after ovulation. Fertilization usually occurs within the fallopian tubes, and any blockage can prevent the fertilized egg from reaching the uterus, leading to complications such as ectopic pregnancies or infertility. Additionally, the cornua help maintain the structural integrity of the uterus and support the passage of menstrual fluid.
The fallopian tubes, also known as oviducts, are a pair of slender tubes that connect the ovaries to the uterus. They play a crucial role in the reproductive system, particularly in the process of fertilization and early embryonic development. Let’s break down the anatomy of the fallopian tube and the specific functions of the cornual end.
Anatomy of the Fallopian Tube
The fallopian tube is divided into several parts:
1.Infundibulum: This is the funnel-shaped opening closest to the ovary, which has finger-like projections called fimbriae that help capture the egg released during ovulation.
2.Ampulla: This is the widest part of the tube, where fertilization typically occurs. It has a larger diameter that allows the egg and sperm to meet.
3.Isthmus: The isthmus is the narrow section of the tube that connects the ampulla to the uterine cavity. It’s where the tubal ligation is often performed for sterilization.
4.Cornual End: This is the portion of the fallopian tube that connects to the uterus. It’s the most proximal part of the tube and is located at the uterine horn.
Cornual blockage in the fallopian tubes can be a significant issue for those trying to conceive, as it can impact fertility. Here are some common causes and factors leading to this condition:
Common Factors Leading to Blockage
1.Pelvic Inflammatory Disease (PID): Infections of the reproductive system, often caused by sexually transmitted infections (STIs) like chlamydia or gonorrhea, can lead to inflammation and scarring in the fallopian tubes.
2.Endometriosis: This condition occurs when tissue similar to the lining of the uterus grows outside the uterus. It can cause adhesions and blockages in the fallopian tubes.
3.Previous Surgeries: Surgical procedures in the pelvic area, such as appendectomies or surgeries for ectopic pregnancies, can lead to scar tissue formation that may block the tubes.
4.Congenital Abnormalities: Some women may be born with anatomical abnormalities in the reproductive tract that can lead to blockages.
Impact of Scar Tissue and Infections
Scar Tissue Formation: Scar tissue, or adhesions, can develop from surgeries, infections, or conditions like endometriosis. This tissue can obstruct the normal pathway of the fallopian tubes, preventing the passage of eggs or sperm.
Fluid Accumulation: In some cases, blockages can lead to a condition known as hydrosalpinx, where fluid accumulates in the fallopian tube due to a blockage, which can further disrupt reproductive functions.
If you or someone you know is dealing with concerns related to fallopian tube blockages, it’s essential to consult a healthcare professional for an accurate diagnosis and potential treatment options.
Cornual block refers to a blockage in the cornua of the uterus, which is the area where the fallopian tubes connect to the uterus. This can lead to infertility and other reproductive issues. Here’s an overview of symptoms, signs of fallopian tube blockage, and how cornual block can be diagnosed.
Symptoms of Cornual Block
1.Infertility: Difficulty conceiving after trying for a year or more.
2.Pelvic Pain: Chronic or intermittent pain in the lower abdomen.
3.Irregular Menstrual Cycles: Changes in the regularity or flow of menstrual periods.
4.Ectopic Pregnancy: A pregnancy that occurs outside the uterus, which may happen if an embryo implants in a blocked fallopian tube.
Advanced Fertility Treatments for Cornual Block
1.In Vitro Fertilization (IVF):
IVF can be a key option for individuals with cornual blockages. In this process, eggs are retrieved from the ovaries and fertilized with sperm in a lab. The resulting embryos are then transferred to the uterus, bypassing the blocked area.
2.Intracytoplasmic Sperm Injection (ICSI):
This is often used alongside IVF, especially in cases of male factor infertility. A single sperm is injected directly into an egg, increasing the chances of fertilization. This can be beneficial when using sperm from a partner or a donor.
3.Surgical Procedures:
Laparoscopy: This minimally invasive surgery can be used to identify and potentially clear blockages in the fallopian tubes. If the blockage is accessible, the surgeon may be able to remove it or treat it.
Salpingostomy: If the blockage is severe, creating a new opening in the fallopian tube may be necessary, allowing for passage of the egg.
4.Fertility Medications:
These can help stimulate ovulation and increase the chances of pregnancy, especially if combined with other treatments.
A cornual block in the fallopian tube refers to a blockage occurring at the junction where the fallopian tube connects to the uterus. This condition can significantly impact fertility because it can prevent sperm from reaching the egg or hinder the passage of a fertilized egg to the uterus, leading to challenges in achieving a successful pregnancy. Women with a cornual block may experience difficulties conceiving naturally and are at an increased risk for ectopic pregnancies if fertilization occurs in the blocked tube.
Diagnosis typically involves imaging techniques like hysterosalpingography (HSG) or laparoscopy, which helps identify the blockage. Treatment options may include surgical procedures to remove the blockage or assistive reproductive technologies such as in vitro fertilization (IVF) when natural conception is not possible. Seeking guidance from a fertility specialist is essential for tailored management and the best chances of conception.
FAQs
1.What causes a cornual block in the fallopian tube?
A cornual block can be caused by several factors, including pelvic inflammatory disease, previous surgeries, endometriosis, or congenital abnormalities.
2.Can a cornual block be diagnosed?
Yes, it can be diagnosed through imaging studies such as HSG, sonohysterography, or laparoscopy, which visualize the fallopian tubes and check for blockages.
3.Is it possible to get pregnant with a cornual block?
While it may be challenging to conceive naturally with a cornual block, there are options available, including surgical treatment or assisted reproductive technologies like IVF.
4.How does a cornual block affect pregnancy risks?
A cornual block increases the risk of ectopic pregnancies if fertilization occurs in the affected tube, as the fertilized egg cannot reach the uterus.